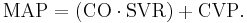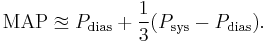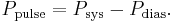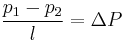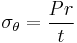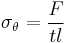Blood pressure
| Blood pressure | |
|---|---|
| Diagnostics | |
A sphygmomanometer, a device used for measuring arterial pressure. |
|
| MeSH | D001795 |
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies between a maximum (systolic) and a minimum (diastolic) pressure.[1] The mean BP, due to pumping by the heart and resistance to flow in blood vessels, decreases as the circulating blood moves away from the heart through arteries. Blood pressure drops most rapidly along the small arteries and arterioles, and continues to decrease as the blood moves through the capillaries and back to the heart through veins.[2] Gravity, valves in veins, and pumping from contraction of skeletal muscles are some other influences on BP at various places in the body.
The measurement blood pressure without further specification usually refers to the systemic arterial pressure measured at a person's upper arm. It is measured on the inside of an elbow at the brachial artery, which is the upper arm's major blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart. A person's BP is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure over diastolic pressure (mmHg), for example 140/90.
Contents |
Systemic arterial blood pressure
Classification
| Category | systolic, mmHg | diastolic, mmHg |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The following classifications of blood pressure are from the American Heart Association, and apply to adults 18 years and older[3] . It assumes the values are a result of averaging seated BP readings measured at 2 or more office visits.[4][5] In the UK, a reading above 140/90 mmHg is considered hypertension.[6]
Normal
While average values for arterial pressure could be computed for any given population, there is often a large variation from person to person; arterial pressure also varies in individuals from moment to moment. Additionally, the average of any given population may have a questionable correlation with its general health; thus the relevance of such average values is equally questionable. However, in a study of 100 human subjects with no known history of hypertension, an average blood pressure of 112/64 mmHg was found,[7] which are currently classified as desirable or "normal" values.
Various factors, such as age and gender influence average values, influence a person's average BP and variations. In children, the normal ranges are lower than for adults and depend on height.[8] As adults age, systolic pressure tends to rise and diastolic tends to fall.[9] In the elderly, BP tends to be above the normal adult range,[10] largely because of reduced flexibility of the arteries. Also, an individual's BP varies with exercise, emotional reactions, sleep, digestion and time of day.
Differences between left and right arm BP measurements tend to be random and average to nearly zero if enough measurements are taken. However, in a small percentage of cases there is a consistent difference greater than 10 mmHg which may need further investigation, e.g. for obstructive arterial disease.[11][12]
The risk of cardiovascular disease increases progressively above 115/75 mmHg.[13] In the past, hypertension was only diagnosed if secondary signs of high arterial pressure were present, along with a prolonged high systolic pressure reading over several visits. Regarding hypotension, in practice blood pressure is considered too low only if noticeable symptoms are present.[14]
Clinical trials demonstrate that people who maintain arterial pressures at the low end of these pressure ranges have much better long term cardiovascular health. The principal medical debate concerns the aggressiveness and relative value of methods used to lower pressures into this range for those who do not maintain such pressure on their own. Elevations, more commonly seen in older people, though often considered normal, are associated with increased morbidity and mortality.
Average blood pressure in (mmHg):
| 1 year | 6–9 years | adults |
|---|---|---|
| 95/65 | 100/65 | 110/65 – 140/90 |
Physiology
There are many physical factors that influence arterial pressure. Each of these may in turn be influenced by physiological factors, such as diet, exercise, disease, drugs or alcohol, stress, obesity, and so-forth.[15]
Some physical factors are:
- Rate of pumping. In the circulatory system, this rate is called heart rate, the rate at which blood (the fluid) is pumped by the heart. The volume of blood flow from the heart is called the cardiac output which is the heart rate (the rate of contraction) multiplied by the stroke volume (the amount of blood pumped out from the heart with each contraction). The higher the heart rate, the higher the mean arterial pressure, assuming no reduction in stroke volume or central venous return.
- Volume of fluid or blood volume, the amount of blood that is present in the body. The more blood present in the body, the higher the rate of blood return to the heart and the resulting cardiac output. There is some relationship between dietary salt intake and increased blood volume, potentially resulting in higher arterial pressure, though this varies with the individual and is highly dependent on autonomic nervous system response and the renin-angiotensin system.
- Resistance. In the circulatory system, this is the resistance of the blood vessels. The higher the resistance, the higher the arterial pressure upstream from the resistance to blood flow. Resistance is related to vessel radius (the larger the radius, the lower the resistance), vessel length (the longer the vessel, the higher the resistance), blood viscosity, as well as the smoothness of the blood vessel walls. Smoothness is reduced by the build up of fatty deposits on the arterial walls. Substances called vasoconstrictors can reduce the size of blood vessels, thereby increasing BP. Vasodilators (such as nitroglycerin) increase the size of blood vessels, thereby decreasing arterial pressure. Resistance, and its relation to volumetric flow rate (Q) and pressure difference between the two ends of a vessel are described by Poiseuille's Law.
- Viscosity, or thickness of the fluid. If the blood gets thicker, the result is an increase in arterial pressure. Certain medical conditions can change the viscosity of the blood. For instance, anemia (low red blood cell concentration), reduces viscosity, whereas increased red blood cell concentration increases viscosity. It had been thought that aspirin and related "blood thinner" drugs decreased the viscosity of blood, but instead studies found[16] that they act by reducing the tendency of the blood to clot.
In practice, each individual's autonomic nervous system responds to and regulates all these interacting factors so that, although the above issues are important, the actual arterial pressure response of a given individual varies widely because of both split-second and slow-moving responses of the nervous system and end organs. These responses are very effective in changing the variables and resulting BP from moment to moment.
Moreover, blood pressure is the result of cardiac output increased by peripheral resistance: blood pressure = cardiac output X peripheral resistance. As a result, an abnormal change in blood pressure is often an indication of a problem affecting the heart's output, the blood vessels' resistance, or both. Thus, knowing the patient's blood pressure is critical to assess any pathology related to output and resistance.
Mean arterial pressure
The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is the average over a cardiac cycle and is determined by the cardiac output (CO), systemic vascular resistance (SVR), and central venous pressure (CVP),[17]
MAP can be approximately determined from measurements of the systolic pressure 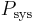 and the diastolic pressure
and the diastolic pressure 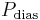 while there is a normal resting heart rate,[17]
while there is a normal resting heart rate,[17]
Pulse pressure
The up and down fluctuation of the arterial pressure results from the pulsatile nature of the cardiac output, i.e. the heartbeat. The pulse pressure is determined by the interaction of the stroke volume of the heart, compliance (ability to expand) of the aorta, and the resistance to flow in the arterial tree. By expanding under pressure, the aorta absorbs some of the force of the blood surge from the heart during a heartbeat. In this way, the pulse pressure is reduced from what it would be if the aorta wasn't compliant.[18] The loss of arterial compliance that occurs with aging explains the elevated pulse pressures found in elderly patients.
The pulse pressure can be simply calculated from the difference of the measured systolic and diastolic pressures,[18]
Arm–leg gradient
The arm–leg (blood pressure) gradient is the difference between the blood pressure measured in the arms and that measured in the legs. It is normally less than 10 mmHg,[19] but may be increased in e.g. coarctation of the aorta.[19]
Vascular resistance
The larger arteries, including all large enough to see without magnification, are conduits with low vascular resistance (assuming no advanced atherosclerotic changes) with high flow rates that generate only small drops in pressure. The smaller arteries and arterioles have higher resistance, and confer the main drop in blood pressure along the circulatory system.
Vascular pressure wave
Modern physiology developed the concept of the vascular pressure wave (VPW). This wave is created by the heart during the systole and originates in the ascending aorta. Much faster than the stream of blood itself, it is then transported through the vessel walls to the peripheral arteries. There the pressure wave can be palpated as the peripheral pulse. As the wave is reflected at the peripheral veins, it runs back in a centripetal fashion. Where the crests of the reflected and the original wave meet, the pressure inside the vessel is higher than the true pressure in the aorta. This concept explains why the arterial pressure inside the peripheral arteries of the legs and arms is higher than the arterial pressure in the aorta,[20][21][22] and in turn for the higher pressures seen at the ankle compared to the arm with normal ankle brachial pressure index values.
Regulation
The endogenous regulation of arterial pressure is not completely understood, but the following mechanisms of regulating arterial pressure have been well-characterized:
- Baroreceptor reflex: Baroreceptors in the high pressure receptor zones (mainly in the aortic arch and carotid sinus) detect changes in arterial pressure. These baroreceptors send signals ultimately to the medulla of the brain stem, specifically to the Rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM). The medulla, by way of the autonomic nervous system, adjusts the mean arterial pressure by altering both the force and speed of the heart's contractions, as well as the total peripheral resistance. The most important arterial baroreceptors are located in the left and right carotid sinuses and in the aortic arch.[23]
- Renin-angiotensin system (RAS): This system is generally known for its long-term adjustment of arterial pressure. This system allows the kidney to compensate for loss in blood volume or drops in arterial pressure by activating an endogenous vasoconstrictor known as angiotensin II.
- Aldosterone release: This steroid hormone is released from the adrenal cortex in response to angiotensin II or high serum potassium levels. Aldosterone stimulates sodium retention and potassium excretion by the kidneys. Since sodium is the main ion that determines the amount of fluid in the blood vessels by osmosis, aldosterone will increase fluid retention, and indirectly, arterial pressure.
- Baroreceptors in low pressure receptor zones (mainly in the venae cavae and the pulmonary veins, and in the atria) result in feedback by regulating the secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH/Vasopressin), renin and aldosterone. The resultant increase in blood volume results an increased cardiac output by the Frank–Starling law of the heart, in turn increasing arterial blood pressure.
These different mechanisms are not necessarily independent of each other, as indicated by the link between the RAS and aldosterone release. Currently, the RAS is targeted pharmacologically by ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists. The aldosterone system is directly targeted by spironolactone, an aldosterone antagonist. The fluid retention may be targeted by diuretics; the antihypertensive effect of diuretics is due to its effect on blood volume. Generally, the baroreceptor reflex is not targeted in hypertension because if blocked, individuals may suffer from orthostatic hypotension and fainting.
Measurement
Arterial pressure is most commonly measured via a sphygmomanometer, which historically used the height of a column of mercury to reflect the circulating pressure.[24] BP values are generally reported in millimetres of mercury (mmHg), though aneroid and electronic devices do not use mercury.
For each heartbeat, BP varies between systolic and diastolic pressures. Systolic pressure is peak pressure in the arteries, which occurs near the end of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles are contracting. Diastolic pressure is minimum pressure in the arteries, which occurs near the beginning of the cardiac cycle when the ventricles are filled with blood. An example of normal measured values for a resting, healthy adult human is 120 mmHg systolic and 80 mmHg diastolic (written as 120/80 mmHg, and spoken [in the US and UK] as "one-twenty over eighty").
Systolic and diastolic arterial BPs are not static but undergo natural variations from one heartbeat to another and throughout the day (in a circadian rhythm). They also change in response to stress, nutritional factors, drugs, disease, exercise, and momentarily from standing up. Sometimes the variations are large. Hypertension refers to arterial pressure being abnormally high, as opposed to hypotension, when it is abnormally low. Along with body temperature, respiratory rate, and pulse rate, BP is one of the four main vital signs routinely monitored by medical professionals and healthcare providers.[25]
Measuring pressure invasively, by penetrating the arterial wall to take the measurement, is much less common and usually restricted to a hospital setting.
Noninvasive
The noninvasive auscultatory and oscillometric measurements are simpler and quicker than invasive measurements, require less expertise, have virtually no complications, are less unpleasant and less painful for the patient. However, noninvasive methods may yield somewhat lower accuracy and small systematic differences in numerical results. Noninvasive measurement methods are more commonly used for routine examinations and monitoring.
Palpation
A minimum systolic value can be roughly estimated by palpation, most often used in emergency situations, but should be used with caution.[26] It has been estimated that, using 50% percentiles, carotid, femoral and radial pulses are present in patients with a systolic blood pressure > 70 mmHg, carotid and femoral pulses alone in patients with systolic blood pressure of > 50 mmHg, and only a carotid pulse in patients with a systolic blood pressure of > 40 mmHg.[26]
A more accurate value of systolic BP can be obtained with a sphygmomanometer and palpating the radial pulse.[27] The diastolic blood pressure cannot be estimated by this method.[28] The American Heart Association recommends that palpation be used to get an estimate before using the auscultatory method.
Auscultatory
The auscultatory method (from the Latin word for "listening") uses a stethoscope and a sphygmomanometer. This comprises an inflatable (Riva-Rocci) cuff placed around the upper arm at roughly the same vertical height as the heart, attached to a mercury or aneroid manometer. The mercury manometer, considered the gold standard, measures the height of a column of mercury, giving an absolute result without need for calibration and, consequently, not subject to the errors and drift of calibration which affect other methods. The use of mercury manometers is often required in clinical trials and for the clinical measurement of hypertension in high-risk patients, such as pregnant women.
A cuff of appropriate size is fitted smoothly and snugly, then inflated manually by repeatedly squeezing a rubber bulb until the artery is completely occluded. Listening with the stethoscope to the brachial artery at the elbow, the examiner slowly releases the pressure in the cuff. When blood just starts to flow in the artery, the turbulent flow creates a "whooshing" or pounding (first Korotkoff sound). The pressure at which this sound is first heard is the systolic BP. The cuff pressure is further released until no sound can be heard (fifth Korotkoff sound), at the diastolic arterial pressure.
The auscultatory method is the predominant method of clinical measurement.[29]
Oscillometric
The oscillometric method was first demonstrated in 1876 and involves the observation of oscillations in the sphygmomanometer cuff pressure[30] which are caused by the oscillations of blood flow, i.e., the pulse.[31] The electronic version of this method is sometimes used in long-term measurements and general practice. It uses a sphygmomanometer cuff, like the auscultatory method, but with an electronic pressure sensor (transducer) to observe cuff pressure oscillations, electronics to automatically interpret them, and automatic inflation and deflation of the cuff. The pressure sensor should be calibrated periodically to maintain accuracy.
Oscillometric measurement requires less skill than the auscultatory technique and may be suitable for use by untrained staff and for automated patient home monitoring.
The cuff is inflated to a pressure initially in excess of the systolic arterial pressure and then reduced to below diastolic pressure over a period of about 30 seconds. When blood flow is nil (cuff pressure exceeding systolic pressure) or unimpeded (cuff pressure below diastolic pressure), cuff pressure will be essentially constant. It is essential that the cuff size is correct: undersized cuffs may yield too high a pressure; oversized cuffs yield too low a pressure. When blood flow is present, but restricted, the cuff pressure, which is monitored by the pressure sensor, will vary periodically in synchrony with the cyclic expansion and contraction of the brachial artery, i.e., it will oscillate. The values of systolic and diastolic pressure are computed, not actually measured from the raw data, using an algorithm; the computed results are displayed.
Oscillometric monitors may produce inaccurate readings in patients with heart and circulation problems, which include arterial sclerosis, arrhythmia, preeclampsia, pulsus alternans, and pulsus paradoxus.
In practice the different methods do not give identical results; an algorithm and experimentally obtained coefficients are used to adjust the oscillometric results to give readings which match the auscultatory results as well as possible. Some equipment uses computer-aided analysis of the instantaneous arterial pressure waveform to determine the systolic, mean, and diastolic points. Since many oscillometric devices have not been validated, caution must be given as most are not suitable in clinical and acute care settings.
The term NIBP, for non-invasive blood pressure, is often used to describe oscillometric monitoring equipment.
White-coat hypertension
For some patients, BP measurements taken in a doctor's office may not correctly characterize their typical BP.[32] In up to 25% of patients, the office measurement is higher than their typical BP. This type of error is called white-coat hypertension (WCH) and can result from anxiety related to an examination by a health care professional.[33] The misdiagnosis of hypertension for these patients can result in needless and possibly harmful medication. WCH can be reduced (but not eliminated) with automated BP measurements over 15 to 20 minutes in a quiet part of the office or clinic.[34]
Debate continues regarding the significance of this effect. Some reactive patients will react to many other stimuli throughout their daily lives and require treatment. In some cases a lower BP reading occurs at the doctor's office.[35]
Home monitoring
Ambulatory blood pressure devices that take readings every half hour throughout the day and night have been used for identifying and mitigating measurement problems like white-coat hypertension. Except for sleep, home monitoring could be used for these purposes instead of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring.[36] Home monitoring may be used to improve hypertension management and to monitor the effects of lifestyle changes and medication related to BP.[4] Compared to ambulatory blood pressure measurements, home monitoring has been found to be an effective and lower cost alternative,[36][37][38] but ambulatory monitoring is more accurate than both clinic and home monitoring in diagnosing hypertension. Ambulatory monitoring is recommended for most patients before the start of antihypertensive drugs.[39]
Aside from the white-coat effect, BP readings outside of a clinical setting are usually slightly lower in the majority of people. The studies that looked into the risks from hypertension and the benefits of lowering BP in affected patients were based on readings in a clinical environment.
When measuring BP, an accurate reading requires that one not drink coffee, smoke cigarettes, or engage in strenuous exercise for 30 minutes before taking the reading. A full bladder may have a small effect on BP readings; if the urge to urinate exists, one should do so before the reading. For 5 minutes before the reading, one should sit upright in a chair with one's feet flat on the floor and with limbs uncrossed. The BP cuff should always be against bare skin, as readings taken over a shirt sleeve are less accurate. During the reading, the arm that is used should be relaxed and kept at heart level, for example by resting it on a table.[40]
Since BP varies throughout the day, measurements intended to monitor changes over longer time frames should be taken at the same time of day to ensure that the readings are comparable. Suitable times are:
- immediately after awakening (before washing/dressing and taking breakfast/drink), while the body is still resting,
- immediately after finishing work.
Automatic self-contained BP monitors are available at reasonable prices, some of which are capable of Korotkoff's measurement in addition to oscillometric methods, enabling irregular heartbeat patients to accurately measure their blood pressure at home.
Invasive
Arterial blood pressure (BP) is most accurately measured invasively through an arterial line. Invasive arterial pressure measurement with intravascular cannulae involves direct measurement of arterial pressure by placing a cannula needle in an artery (usually radial, femoral, dorsalis pedis or brachial).
The cannula must be connected to a sterile, fluid-filled system, which is connected to an electronic pressure transducer. The advantage of this system is that pressure is constantly monitored beat-by-beat, and a waveform (a graph of pressure against time) can be displayed. This invasive technique is regularly employed in human and veterinary intensive care medicine, anesthesiology, and for research purposes.
Cannulation for invasive vascular pressure monitoring is infrequently associated with complications such as thrombosis, infection, and bleeding. Patients with invasive arterial monitoring require very close supervision, as there is a danger of severe bleeding if the line becomes disconnected. It is generally reserved for patients where rapid variations in arterial pressure are anticipated.
Invasive vascular pressure monitors are pressure monitoring systems designed to acquire pressure information for display and processing. There are a variety of invasive vascular pressure monitors for trauma, critical care, and operating room applications. These include single pressure, dual pressure, and multi-parameter (i.e. pressure / temperature). The monitors can be used for measurement and follow-up of arterial, central venous, pulmonary arterial, left atrial, right atrial, femoral arterial, umbilical venous, umbilical arterial, and intracranial pressures.
Fetal blood pressure
In pregnancy, it is the fetal heart and not the mother's heart that builds up the fetal BP to drive its blood through the fetal circulation.
The BP in the fetal aorta is approximately 30 mmHg at 20 weeks of gestation, and increases to approximately 45 mmHg at 40 weeks of gestation.[41]
The average BP for full-term infants:
Systolic 65–95 mm Hg
Diastolic 30–60 mm Hg[42]
Blood pressure is the measurement of force that is applied to the walls of the blood vessels as the heart pumps blood throughout the body.[43] The human circulatory system is 60,000 miles long, and the magnitude of blood pressure is not uniform in all the blood vessels in the human body. The blood pressure is determined by the diameter, flexibility and the amount of blood being pumped through the blood vessel.[43] Blood pressure is also affected by other factors including exercise, stress level, diet and sleep.
The average normal blood pressure in the brachial artery, which is the next direct artery from the aorta after the subclavian artery, is 120mmHg/80mmHg. Blood pressure readings are measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) using sphygmomanometer. Two pressures are measured and recorded namely as systolic and diastolic pressures. Systolic pressure reading is the first reading, which represents the maximum exerted pressure on the vessels when the heart contracts, while the diastolic pressure, the second reading, represents the minimum pressure in the vessels when the heart relaxes.[44] Other major arteries have similar levels of blood pressure recordings indicating very low disparities among major arteries. The innominate artery, the average reading is 110/70mmHg, the right subclavian artery averages 120/80 and the abdominal aorta is 110/70mmHg.[45] The relatively uniform pressure in the arteries indicate that these blood vessels act as a pressure reservoir for fluids that are transported within them.
Pressure drops gradually as blood flows from the major arteries, through the arterioles, the capillaries until blood is pushed up back into the heart via the venules, the veins through the vena cava with the help of the muscles. At any given pressure drop, the flow rate is determined by the resistance to the blood flow. In the arteries, with the absence of diseases, there is very little or no resistance to blood. The vessel diameter is the most principal determinant to control resistance. Compared to other smaller vessels in the body, the artery has a much bigger diameter (4mm), therefore the resistance is low.[45]
In addition, flow rate (Q) is also the product of the cross-sectional area of the vessel and the average velocity (Q=AV). Flow rate is directly proportional to the pressure drop in a tube or in this case a vessel. ∆P α Q. The relationship is further described by Poisseulle’s equation ∆P=8µlQ/πr^4.[46] As evident in the Poisseulle’s equation, although flow rate is proportional to the pressure drop, there are other factors of blood vessels that contribute towards the difference in pressure drop in bifurcations of blood vessels. These include viscosity, length of the vessel, and radius of the vessel.
Factors that determine the flow’s resistance as described by Poiseuille’s relationship:
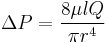
- ∆P: Pressure drop/gradient
- µ: Viscosity
- l: length of tube. In the case of vessels with infinitely long lengths, l is replaced with diameter of the vessel.
- Q: flow rate of the blood in the vessel
- r: radius of the vessel
Assuming steady, laminar flow in the vessel, the blood vessels behavior is similar to that of a pipe. For instance if p1 and p2 are pressures are at the ends of the tube, the pressure drop/gradient is:[47]
In the arterioles blood pressure is lower than in the major arteries. This is due to bifurcations, which cause a drop in pressure. The more bifurcations, the higher the total cross-sectional area, therefore the pressure across the surface drops. This is why the arterioles have the highest pressure-drop. The pressure drop of the arterioles is the product of flow rate and resistance: ∆P=Q xresistance. The high resistance observed in the arterioles, which factor largely in the ∆P is a result of a smaller radius of about 30 µm.[48] The smaller the radius of a tube, the larger the resistance to fluid flow.
Immediately following the arterioles are the capillaries. Following the logic obvserved in the arterioles, we expect the blood pressure to be lower in the capillaries compared to the arterioles. Since pressure is a function of force per unit area, (P=F/A), the larger the surface area, the lesser the pressure when an external force acts on it. Though the radii of the capillaries are very small, the network of capillaries have the largest surface area in the vascular network. They are known to have the largest surface area (485mm) in the human vascular network. The larger the total cross-sectional area, the lower the mean velocity as well as the pressure.[45]
Reynold’s number also affects the blood flow in capillaries. Due to its smaller radius and lowest velocity compared to other vessels, the Reynold’s number at the capillaries is very low, resulting in laminar instead of turbulent flow.[49]
The Reynold’s number (denoted NR or Re) is a relationship that helps determine the behavior of a fluid in a tube, in this case blood in the vessel. The equation for this dimensionless relationship is written as:[46]
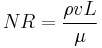
- ρ: density of the blood
- v: mean velocity of the blood
- L: characteristic dimension of the vessel, in this case diameter
- μ: viscosity of blood
The Reynold’s number is directly proportional to the velocity and diameter of the tube. Note that NR is directly proportional to the mean velocity as well as the diameter. A Reynold’s number of less than 2300 is laminar fluid flow, which is characterized by constant flow motion, where as a value of over 4000, is represented as turbulent flow. Turbulent flow is characterized as chaotic and irregular flow.[46]
Disorders
Disregulation disorders of blood pressure control include high blood pressure, blood pressure that is too low, and blood pressure that shows excessive or maladaptive fluctuation.
High
Arterial hypertension can be an indicator of other problems and may have long-term adverse effects. Sometimes it can be an acute problem, for example hypertensive emergency.
All levels of arterial pressure put mechanical stress on the arterial walls. Higher pressures increase heart workload and progression of unhealthy tissue growth (atheroma) that develops within the walls of arteries. The higher the pressure, the more stress that is present and the more atheroma tend to progress and the heart muscle tends to thicken, enlarge and become weaker over time.
Persistent hypertension is one of the risk factors for strokes, heart attacks, heart failure and arterial aneurysms, and is the leading cause of chronic renal failure. Even moderate elevation of arterial pressure leads to shortened life expectancy. At severely high pressures, mean arterial pressures 50% or more above average, a person can expect to live no more than a few years unless appropriately treated.[50]
In the past, most attention was paid to diastolic pressure; but nowadays it is recognised that both high systolic pressure and high pulse pressure (the numerical difference between systolic and diastolic pressures) are also risk factors. In some cases, it appears that a decrease in excessive diastolic pressure can actually increase risk, due probably to the increased difference between systolic and diastolic pressures (see the article on pulse pressure). If systolic blood pressure is elevated (>140) with a normal diastolic blood pressure (<90), it is called "isolated systolic hypertension" and may present a health concern.[51][52]
For those with heart valve regurgitation, a change in its severity may be associated with a change in diastolic pressure. In a study of people with heart valve regurgitation that compared measurements 2 weeks apart for each person, there was an increased severity of aortic and mitral regurgitation when diastolic blood pressure increased, whereas when diastolic blood pressure decreased, there was a decreased severity.[53]
Low
Blood pressure that is too low is known as hypotension. The similarity in pronunciation with hypertension can cause confusion. Hypotension is a medical concern only if it causes signs or symptoms, such as dizziness, fainting, or in extreme cases, shock.[5]
When arterial pressure and blood flow decrease beyond a certain point, the perfusion of the brain becomes critically decreased (i.e., the blood supply is not sufficient), causing lightheadedness, dizziness, weakness or fainting.
Sometimes the arterial pressure drops significantly when a patient stands up from sitting. This is known as orthostatic hypotension (postural hypotension); gravity reduces the rate of blood return from the body veins below the heart back to the heart, thus reducing stroke volume and cardiac output.
When people are healthy, the veins below their heart quickly constrict and the heart rate increases to minimize and compensate for the gravity effect. This is carried out involuntarily by the autonomic nervous system. The system usually requires a few seconds to fully adjust and if the compensations are too slow or inadequate, the individual will suffer reduced blood flow to the brain, dizziness and potential blackout. Increases in G-loading, such as routinely experienced by aerobatic or combat pilots 'pulling Gs', greatly increases this effect. Repositioning the body perpendicular to gravity largely eliminates the problem.
Other causes of low arterial pressure include:
- Sepsis
- Hemorrhage - blood loss
- Toxins including toxic doses of BP medicine
- Hormonal abnormalities, such as Addison's disease
- Eating disorders, particularly anorexia nervosa and bulimia
Shock is a complex condition which leads to critically decreased perfusion. The usual mechanisms are loss of blood volume, pooling of blood within the veins reducing adequate return to the heart and/or low effective heart pumping. Low arterial pressure, especially low pulse pressure, is a sign of shock and contributes to and reflects decreased perfusion.
If there is a significant difference in the pressure from one arm to the other, that may indicate a narrowing (for example, due to aortic coarctation, aortic dissection, thrombosis or embolism) of an artery .
Fluctuating blood pressure
Normal fluctuation in blood pressure is adaptive and necessary. Fluctuations in pressure that are significantly greater than the norm are associated with greater white matter hyperintensity, a finding consistent with reduced local cerebral blood flow[54] and a heightened risk of cerebrovascular disease.[55] Within both high- and low-blood pressure groups, a greater degree of fluctuation was found to correlate with an increase in cerebrovascular disease compared to those with less variability, suggesting the consideration of the clinical management of blood pressure fluctuations, even among normotensive older adults.[56] Older individuals and those who had received blood pressure medications were more likely to exhibit larger fluctuations in pressure.[57]
At other sites
| Site | Normal pressure range (in mmHg)[58] |
|
|---|---|---|
| Central venous pressure | 3–8 | |
| Right ventricular pressure | systolic | 15–30 |
| diastolic | 3–8 | |
| Pulmonary artery pressure | systolic | 15–30 |
| diastolic | 4–12 | |
| Pulmonary vein/ |
2–15 | |
| Left ventricular pressure | systolic | 100–140 |
| diastolic | 3-12 | |
Blood pressure generally refers to the arterial pressure in the systemic circulation. However, measurement of pressures in the venous system and the pulmonary vessels plays an important role in intensive care medicine but requires an invasive central venous catheter.
Systemic venous pressure
Venous pressure is the vascular pressure in a vein or in the atria of the heart. It is much less than arterial pressure, with common values of 5 mmHg in the right atrium and 8 mmHg in the left atrium.
Variants of venous pressure include:
- Central venous pressure, which is a good approximation of right atrial pressure,[59] which is a major determinant of right ventricular end diastolic volume. (However, there can be exceptions in some cases.)[60]
- The jugular venous pressure (JVP) is the indirectly observed pressure over the venous system. It can be useful in the differentiation of different forms of heart and lung disease.
- The portal venous pressure is the blood pressure in the portal vein. It is normally 5–10 mm Hg[61]
Pulmonary pressure
Normally, the pressure in the pulmonary artery is about 15 mmHg at rest.[62]
Increased BP in the capillaries of the lung cause pulmonary hypertension, with interstitial edema if the pressure increases to above 20 mmHg, and to frank pulmonary edema at pressures above 25 mmHg.[63]
Relation to wall tension
Regardless of site, blood pressure is related to the wall tension of the vessel according to the Young–Laplace equation (assuming that the vessel wall is very small as compared to the diameter of the lumen):
where
- P is the blood pressure
- t is the wall thickness
- r is the inside radius of the cylinder.
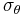 is the cylinder stress or "hoop stress".
is the cylinder stress or "hoop stress".
For the thin-walled assumption to be valid the vessel must have a wall thickness of no more than about one-tenth (often cited as one twentieth) of its radius.
The cylinder stress, in turn, is the average force exerted circumferentially (perpendicular both to the axis and to the radius of the object) in the cylinder wall, and can be described as:
where:
- F is the force exerted circumferentially on an area of the cylinder wall that has the following two lengths as sides:
- t is the radial thickness of the cylinder
- l is the axial length of the cylinder
References
- ^ "Normal Blood Pressure Range Adults". Health and Life. http://healthlifeandstuff.com/2010/06/normal-blood-pressure-range-adults/.
- ^ Klabunde, Richard (2005). Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. pp. 93–4. ISBN 978-0781750301.
- ^ "Understanding blood pressure readings". American Heart Association. 11 January 2011. http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/Conditions/HighBloodPressure/AboutHighBloodPressure/Understanding-Blood-Pressure-Readings_UCM_301764_Article.jsp. Retrieved 30 March 2011.
- ^ a b Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR et al. (December 2003). "Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure". Hypertension 42 (6): 1206–52. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000107251.49515.c2. PMID 14656957. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/hypertension/.
- ^ a b "Diseases and conditions index - hypotension". National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. September 2008. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/dci/Diseases/hyp/hyp_whatis.html. Retrieved 2008-09-16.
- ^ "Hypertension: management of hypertension in adults in primary care". NICE clinical guideline 34. London: National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE). June 2006. http://www.nice.org.uk/nicemedia/pdf/CG034NICEguideline.pdf. Retrieved 2008-09-15.
- ^ Pesola GR, Pesola HR, Nelson MJ, Westfal RE (January 2001). "The normal difference in bilateral indirect BP recordings in normotensive individuals". American Journal of Emergency Medicine 19 (1): 43–5. doi:10.1053/ajem.2001.20021. PMID 11146017. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6W9K-45SRDHC-C&_user=10&_coverDate=01%2F31%2F2001&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=74f2b32e088d88986cd307f6c7219331.
- ^ National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Blood pressure tables for children and adolescents. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/guidelines/hypertension/child_tbl.htm. (Note that the median BP is given by the 50th percentile and hypertension is defined by the 95th percentile for a given age, height, and gender.)
- ^ (Pickering et al. 2005, p. 145) See Isolated Systolic Hypertension.
- ^ "...more than half of all Americans aged 65 or older have hypertension." (Pickering et al. 2005, p. 144)
- ^ Eguchi K, Yacoub M, Jhalani J, Gerin W, Schwartz JE, Pickering TG (February 2007). "Consistency of blood pressure differences between the left and right arms". Arch Intern Med 167 (4): 388–93. doi:10.1001/archinte.167.4.388. PMID 17325301. http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/167/4/388.
- ^ Agarwal R, Bunaye Z, Bekele DM (March 2008). "Prognostic significance of between-arm blood pressure differences". Hypertension 51 (3): 657–62. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.104943. PMID 18212263.
- ^ Appel LJ, Brands MW, Daniels SR, Karanja N, Elmer PJ, Sacks FM (February 2006). "Dietary approaches to prevent and treat hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association". Hypertension 47 (2): 296–308. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000202568.01167.B6. PMID 16434724.
- ^ Mayo Clinic staff (2009-05-23). "Low blood pressure (hypotension) — Causes". MayoClinic.com. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/low-blood-pressure/DS00590/DSECTION=causes. Retrieved 2010-10-19.
- ^ [1]
- ^ Rosenson RS, Wolff D, Green D, Boss AH, Kensey KR (February 2004). "Aspirin. Aspirin does not alter native blood viscosity". J. Thromb. Haemost. 2 (2): 340–1. doi:10.1111/j.1538-79333.2004.0615f.x. PMID 14996003.
- ^ a b Klabunde, RE (2007). "Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts - Mean Arterial Pressure". http://www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP006.htm. Retrieved 2008-09-29. Archived version 2009-10-03
- ^ a b Klabunde, RE (2007). "Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts - Pulse Pressure". http://www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP003.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-02. Archived version 2009-10-03
- ^ a b Markham LW, Knecht SK, Daniels SR, Mays WA, Khoury PR, Knilans TK (November 2004). "Development of exercise-induced arm-leg blood pressure gradient and abnormal arterial compliance in patients with repaired coarctation of the aorta". Am. J. Cardiol. 94 (9): 1200–2. doi:10.1016/j.amjcard.2004.07.097. PMID 15518624.
- ^ Messerli FH, Williams B, Ritz E (2007). "Essential hypertension". Lancet 370 (9587): 591–603. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61299-9. PMID 17707755.
- ^ O'Rourke M (1 July 1995). "Mechanical principles in arterial disease". Hypertension 26 (1): 2–9. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.26.1.2. PMID 7607724. http://hyper.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/full/26/1/2.
- ^ Mitchell GF (2006). "Triangulating the peaks of arterial pressure". Hypertension 48 (4): 543–5. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000238325.41764.41. PMID 16940226. http://hyper.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/full/48/4/543.
- ^ Klabunde, RE (2007). "Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts - Arterial Baroreceptors". http://www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP012.htm. Retrieved 2008-09-09. Archived version 2009-10-03
- ^ Booth, J (1977). "A short history of blood pressure measurement". Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine 70 (11): 793–9. PMC 1543468. PMID 341169. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1543468.
- ^ "Vital Signs (Body Temperature, Pulse Rate, Respiration Rate, Blood Pressure)". OHSU Health Information. Oregon Health & Science University. http://www.ohsu.edu/xd/health/health-information/topic-by-id.cfm?ContentTypeId=85&ContentId=P00866. Retrieved 2010-04-16.
- ^ a b Deakin CD, Low JL (September 2000). "Accuracy of the advanced trauma life support guidelines for predicting systolic blood pressure using carotid, femoral, and radial pulses: observational study". BMJ 321 (7262): 673–4. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7262.673. PMC 27481. PMID 10987771. http://bmj.com/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10987771.
- ^ Interpretation - Blood Pressure - Vitals, University of Florida. Retrieved 2008-03-18.
- ^ G8 Secondary Survey, "Manitoba". Retrieved 2008-03-18.
- ^ (Pickering et al. 2005, p. 146) See Blood Pressure Measurement Methods.
- ^ (Pickering et al. 2005, p. 147) See The Oscillometric Technique.
- ^ Laurent, P (2003-09-28). "Blood Pressure & Hypertension". http://www.blood-pressure-hypertension.com/how-to-measure/measure-blood-pressure-8.shtml. Retrieved 2009-10-05.
- ^ Elliot, Victoria Stagg (2007-06-11). "Blood pressure readings often unreliable". American Medical News (American Medical Association). http://www.ama-assn.org/amednews/2007/06/11/hlsa0611.htm. Retrieved 2008-08-16.
- ^ Jhalani, Juhee, Tanya Goyal et al. (2005). "Anxiety and outcome expectations predict the white-coat effect". Blood Pressure Monitoring 10 (6): 317–9. doi:10.1097/00126097-200512000-00006. PMID 16496447. http://journals.lww.com/bpmonitoring/pages/articleviewer.aspx?year=2005&issue=12000&article=00006&type=abstract. Retrieved 2009-10-03.
- ^ (Pickering et al. 2005, p. 145) See White Coat Hypertension or Isolated Office Hypertension.
- ^ (Pickering et al. 2005, p. 146) See Masked Hypertension or Isolated Ambulatory Hypertension.
- ^ a b Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A et al. (June 2007). "2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)". Eur Heart J 28 (12): 1462–536. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm236. PMID 17562668.
- ^ Niiranen, TJ, Kantola IM et al. (2006). "A comparison of home measurement and ambulatory monitoring of blood pressure in the adjustment of antihypertensive treatment". Am J Hypertens 19 (5): 468–74. doi:10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.10.017. PMID 16647616.
- ^ Shimbo, Daichi, Thomas G. Pickering et al. (2007). "The Relative Utility of Home, Ambulatory, and Office Blood Pressures in the Prediction of End-Organ Damage". Am J Hypertens 20 (5): 476–82. doi:10.1016/j.amjhyper.2006.12.011. PMC 1931502. PMID 17485006. http://www.nature.com/ajh/journal/v20/n5/abs/ajh200783a.html.
- ^ Kate Lovibond, Sue Jowett, Pelham Barton, Mark Caulfield et al. "Cost-effectiveness of options for the diagnosis of high blood pressure in primary care: a modelling study", The Lancet, 24 August 2011. Retrieved 24 August 2011.
- ^ National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Tips for having your blood pressure taken. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/hbp/detect/tips.htm.
- ^ Struijk PC, Mathews VJ, Loupas T et al. (October 2008). "Blood pressure estimation in the human fetal descending aorta". Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 32 (5): 673–81. doi:10.1002/uog.6137. PMID 18816497.
- ^ Sharon, S. M. & Emily, S. M.(2006). Foundations of Maternal-Newborn Nursing. (4th ed p.476). Philadelphia:Elsevier.
- ^ a b Dugdale, David. "Blood Pressure". http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/003398.htm. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ Klabunde, Richard. "Arterial Blood Pressure". http://www.cvphysiology.com/Blood%20Pressure/BP002.htm. Retrieved 31 March 2011.
- ^ a b c Fung, Yuan-cheng (1997). Biomechanics:Circulation. New York: Springer. p. 571. ISBN 0387943846.
- ^ a b c Munson; Young, Okiishi, Huebsch (2009). Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics (Sixth ed.). New Jersey: John Wiley &Sons, Inc.. p. 725. ISBN 9780470262849.
- ^ Womersley, J. R. (1955). "Method for the calculation of velocity, rate of flow and viscous drag in arteries when the pressure gradient is known". Journal of Physiology 127 (3): 553–563. PMC 1365740. PMID 14368548. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1365740.
- ^ Sircar, Sabyasach (2008). Principles of Medical Physiology. India: vistasta Publishing. ISBN 9781588905727.
- ^ Fung, Yuan-cheng; Zweifach, B.W. (1971). "Microcirculation: Mechanics of Blood Flow in Capillaries". Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics 3: 189–210. doi:10.1146/annurev.fl.03.010171.001201.
- ^ Textbook of Medical Physiology, 7th Ed., Guyton & Hall, Elsevier-Saunders, ISBN 0-7216-0240-1, page 220.
- ^ "Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern? - MayoClinic.com". http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hypertension/AN01113. Retrieved 2011-12-07.
- ^ "Clinical Management of Isolated Systolic Hypertension". http://web.archive.org/web/20081218160455/http://www.clevelandclinicmeded.com/medicalpubs/diseasemanagement/nephrology/isosystolic/isosystolic.htm. Retrieved 2011-12-07.
- ^ Gottdiener JS, Panza JA, St John Sutton M, Bannon P, Kushner H, Weissman NJ (July 2002). "Testing the test: The reliability of echocardiography in the sequential assessment of valvular regurgitation". American Heart Journal 144 (1): 115–21. doi:10.1067/mhj.2002.123139. PMID 12094197. http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/439534. Retrieved 2010-06-30.
- ^ Thomas, A.J., Perry, R., Barber, R., Kalaria, R.N., O’Brien, J.T. (2002) "Pathologies and pathological mechanisms for white matter hyperintensities in depression," ' 'Ann N Y Acad Sci., 977:333–339.
- ^ Brickman AM, Reitz C, Luchsinger JA, Manly JJ, Schupf N, Muraskin J, DeCarli C, Brown TR, Mayeux R. Long-term blood pressure fluctuation and cerebrovascular disease in an elderly cohort. Arch Neurol. 2010 May;67(5):564-9 PMID 20457955 PMCID PMC2917204 Free Full Text: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2917204/?tool=pubmed NIHMSID NIHMS216309 http://archneur.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/short/67/5/564
- ^ Brickman AM, Reitz C, Luchsinger JA, Manly JJ, Schupf N, Muraskin J, DeCarli C, Brown TR, Mayeux R. Long-term blood pressure fluctuation and cerebrovascular disease in an elderly cohort. Arch Neurol. 2010 May;67(5):564-9 PMID 20457955 PMCID PMC2917204 Free Full Text: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2917204/?tool=pubmed NIHMSID NIHMS216309 http://archneur.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/short/67/5/564
- ^ Brickman AM, Reitz C, Luchsinger JA, Manly JJ, Schupf N, Muraskin J, DeCarli C, Brown TR, Mayeux R. Long-term blood pressure fluctuation and cerebrovascular disease in an elderly cohort. Arch Neurol. 2010 May;67(5):564-9 PMID 20457955 PMCID PMC2917204 Free Full Text: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2917204/?tool=pubmed NIHMSID NIHMS216309 http://archneur.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/short/67/5/564
- ^ Table 30-1 in: Trudie A Goers; Washington University School of Medicine Department of Surgery; Klingensmith, Mary E; Li Ern Chen; Sean C Glasgow (2008). The Washington manual of surgery. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0-7817-7447-0.
- ^ "Central Venous Catheter Physiology". http://www.healthsystem.virginia.edu/internet/anesthesiology-elective/cardiac/cvcphys.cfm. Retrieved 2009-02-27.
- ^ Tkachenko BI, Evlakhov VI, Poyasov IZ (2002). "Independence of changes in right atrial pressure and central venous pressure". Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 134 (4): 318–20. doi:10.1023/A:1021931508946. PMID 12533747.
- ^ "Esophageal Varices : Article Excerpt by: Samy A Azer". eMedicine. http://www.emedicine.com/med/byname/esophageal-varices.htm. Retrieved 2011-08-22.
- ^ What Is Pulmonary Hypertension? From Diseases and Conditions Index (DCI). National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Last updated September 2008. Retrieved on 6 April 2009.
- ^ Chapter 41, page 210 in: Cardiology secrets By Olivia Vynn Adair Edition: 2, illustrated Published by Elsevier Health Sciences, 2001 ISBN 1560534206, 9781560534204
Further reading
- Pickering, TG; Hall, JE; Appel, LJ et al. (2005). "Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: Part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the Subcommittee of Professional and Public Education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research". Hypertension 45 (5): 142–61. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000150859.47929.8e. PMID 15611362. http://hyper.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/full/45/1/142. Retrieved 2009-10-01.
External links
- Blood Pressure Association (UK)
- British Hypertension Society: list of validated blood pressure monitors
- Pulmonary Hypertension Cleveland Clinic
- American Heart Association
- Control of Blood Pressure
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||